TIG Welding
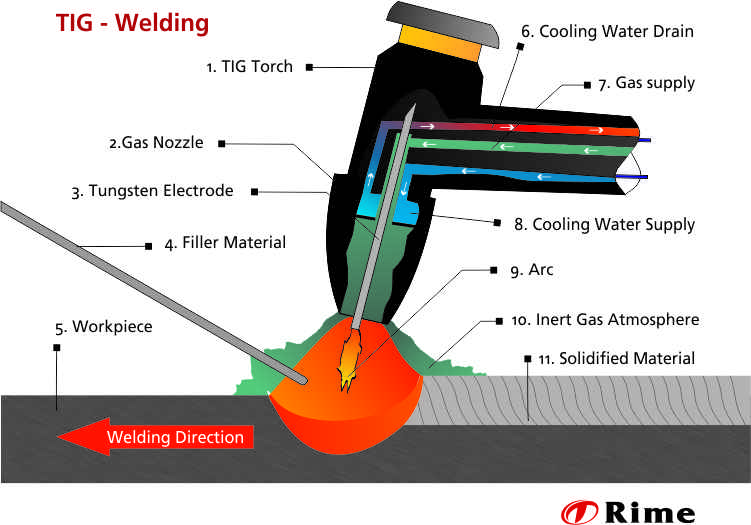
TIG welding belongs to the fusion welding procedures. It is suitable for universal application and is characterised by its clean processing. With this method, only a few sprayings and almost no gases are produced. When welding a workpiece, the necessary electric current is supplied via a tungsten electrode. In opposite to MIG and MAG welding, this electrode does not melt away.
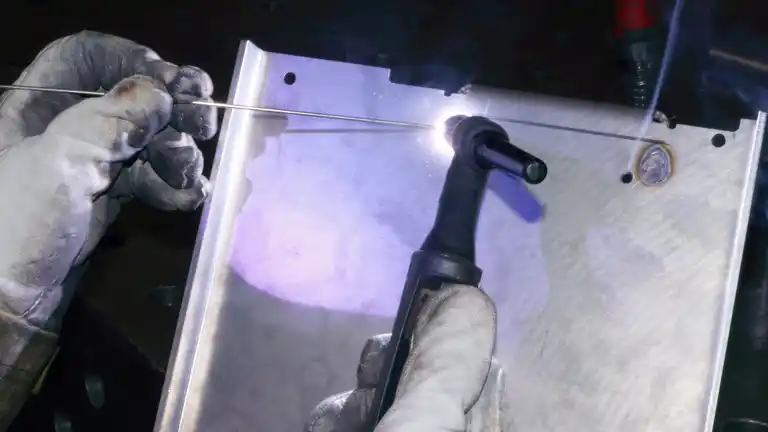

The weld seams are of very high quality, because the molten metal is protected from the influence of oxygen by the supply of a shielding gas.
The supply takes place directly via the welding head . As the electrode does not melt off, the filler metal is fed manually. With TIG welding, the welder can adjust the current intensity and the amount of filler metal to the workpiece. In TIG welding, the filler metal is fed continuously or drop by drop. The welding wire remains continuously in the liquid weld pool. This is why it is also called the "pushing method".
Technical details
TIG welding is possible with direct or alternating current
Welding with direct current
Welding with direct current is the most commonly used method. Here the tungsten electrode lies on the negative pole. This form of welding is used to join alloyed steels or non-ferrous metals such as copper or brass.
Welding with alternating current
Alternating current is used to join light metals such as aluminium and magnesium, because the oxide layer is broken up. In exceptional cases, light metals are also welded with direct current, with the electrode resting on the positive pole.
In general, however, it can be stated that each metal suitable for fusion welding procedure can be welded using the TIG procedure. As tungsten inert gas welding can be used both manually and as an automated process, this procedure is used in very many areas.
Large opportunities for its use are found in the aerospace industry, in structural steelwork and railing construction as well as in pipe laying. TIG welding is always used if particularly high weld quality and properties are required. This work can be done using two hands in manual welding.
One hand is used to add the filler metal while the other hand holds the welding torch. As the skill requirements are very high, these tasks are only carried out by specialised welders.
Advantages
No slags are produced when the inert gases argon and helium are used. This welding procedures is very fast. This means that the material hardly deforms at all due to the short heat effect. TIG welding can be used in all positions.
Disadvantages
This welding procedure is very susceptible to wind. For this reason, TIG welding cannot be used outdoors. The action of wind can blow the shielding gas away, which then results in increased oxidation of the weld. Such welds are nowhere near as durable as welds welded under shielding gas. Rust must always be removed during the weld preparation.
Contact us!
Call or write us an email if you have questions about welding or need a quote!